Cloud Computing: Advantages, Risks, and Implementation in Enterprises
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses manage and store data. With the ability to access computing resources on-demand, enterprises can scale operations efficiently while reducing IT costs. This article explores the benefits, risks, and implementation of cloud computing in enterprises. It also compares top cloud service providers—AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure—and discusses the significance of hybrid cloud and edge computing.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
-
Cost Efficiency Cloud computing reduces the need for physical infrastructure, lowering capital expenditure and operational costs. Businesses only pay for the resources they use, making it a cost-effective solution.
-
Scalability and Flexibility Cloud services allow businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility ensures optimal performance and cost savings.
-
Accessibility and Collaboration Cloud computing enables employees to access data and applications from anywhere, fostering remote work and collaboration across teams.
-
Security and Compliance Leading cloud providers offer robust security measures, including encryption, identity management, and compliance with global standards such as GDPR and HIPAA.
-
Disaster Recovery and Backup Cloud solutions provide automated backups and disaster recovery mechanisms, ensuring business continuity even in case of hardware failures.
Risks of Cloud Computing
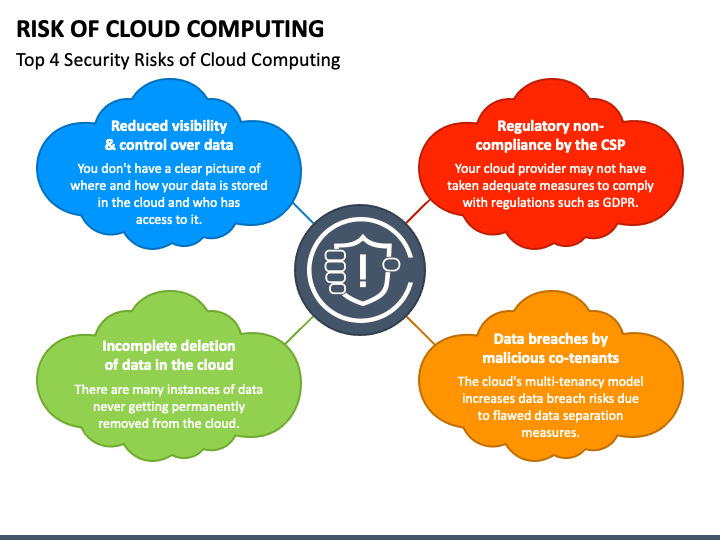
-
Data Security and Privacy Concerns Storing sensitive data on the cloud poses security risks. Enterprises must ensure data encryption and implement access controls.
-
Downtime and Service Reliability Cloud outages can disrupt business operations. Selecting providers with high availability guarantees and redundancy options mitigates this risk.
-
Vendor Lock-in Migrating between cloud providers can be complex and costly. Businesses should consider multi-cloud strategies to avoid dependence on a single provider.
-
Regulatory Compliance Challenges Different regions have varying data protection laws. Enterprises must choose cloud solutions that comply with industry regulations.
-
Limited Control Cloud providers manage infrastructure, limiting direct control over hardware and software configurations.
Implementing Cloud Computing in Enterprises
-
Assess Business Needs Organizations must evaluate workloads, compliance requirements, and performance needs before migrating to the cloud.
-
Choose the Right Cloud Model Enterprises can opt for public, private, or hybrid cloud solutions based on their needs.
-
Select a Cloud Provider Comparing cloud service providers helps businesses choose the best fit for their infrastructure and budget.
-
Develop a Migration Strategy A phased migration approach ensures minimal disruption and successful cloud adoption.
-
Implement Security Measures Enterprises should enforce strong authentication, encryption, and regular security audits to protect cloud data.
Comparison of Top Cloud Service Providers
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is the market leader in cloud computing, offering a vast range of services including computing, storage, AI, and networking. It provides extensive global coverage, reliability, and a mature ecosystem. However, AWS pricing can be complex, and its steep learning curve requires expertise.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP is known for its AI and data analytics capabilities. It integrates seamlessly with Google services and offers competitive pricing. While it excels in machine learning, GCP has a smaller market share than AWS and Azure.
Microsoft Azure
Azure provides deep integration with Microsoft products, making it ideal for enterprises using Windows environments. It offers hybrid cloud solutions and strong security features. However, Azure’s complexity may require specialized skills.
Hybrid Cloud and Edge Computing
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud environments, offering greater flexibility and control. Businesses benefit from cost savings while maintaining sensitive data on-premises. It is ideal for organizations with regulatory requirements.
Edge Computing
Edge computing processes data closer to the source rather than relying on centralized cloud servers. This reduces latency and improves real-time processing, making it essential for IoT applications and AI-driven operations.
Cloud computing provides unparalleled advantages for enterprises, including cost efficiency, scalability, and security. However, risks such as data security and vendor lock-in must be managed effectively. By selecting the right cloud provider and implementing a strategic approach, businesses can leverage cloud computing for innovation and growth. Additionally, hybrid cloud and edge computing offer advanced solutions to enhance performance and security in modern enterprises.